
Autonomous Photovoltaic Systems and Their Construction
Autonomous photovoltaic systems (houses, caravans, etc.)
In areas without access to the public electricity grid, the energy needs of a facility, such as a house, can be met by an autonomous photovoltaic system. Additionally, we can also distinguish hybrid systems, where photovoltaic panels are combined with other energy sources, such as wind energy or diesel generators.
An autonomous photovoltaic system is a unit that generates electricity exclusively from photovoltaic generators. These systems can be categorized into two groups: those that have an energy storage unit (usually batteries) and those that directly supply the loads without storage (e.g., a vacation home with a DC water pump connected directly to a photovoltaic panel).
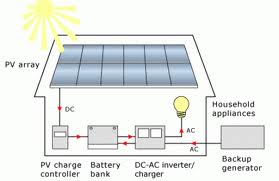
The key components of an autonomous system include:
- Photovoltaic panels
- Batteries
- Charge controller
- DC/AC inverter (for 230 volts)
- Fuses
- DC switches
- Instruments to measure battery capacity
The DC circuit usually operates at voltages of 12, 24, or 48 volts.
Estimating Photovoltaic System Production
Hybrid autonomous photovoltaic system: Such a system is often chosen because of cost considerations. Photovoltaics can power facilities (like vacation homes), but the cost can be high. Therefore, photovoltaic systems are combined with other energy sources.
For example, in areas with good wind potential, wind turbines and photovoltaics can work together, especially when sunlight is limited. In this case, both energy sources charge the batteries via charge controllers, and the energy is then used to power the facility's needs, such as in an autonomous photovoltaic home.
In general, the technologies involved in hybrid systems for energy autonomy include photovoltaics, wind turbines, and diesel or gasoline generators. The energy sources are connected in parallel to the local grid to ensure uninterrupted power supply. The choice of such a system is based on an analysis of meteorological and economic factors.
Autonomous System Construction
Autonomous photovoltaic systems (or off-grid systems) provide energy autonomy to facilities that do not have access to the public grid. There are various categories of off-grid photovoltaic systems, such as:
- Houses located far from the grid with prohibitively high connection costs.
- Houses that, for various reasons, cannot be electrified.
- Agricultural or livestock units located far from the grid.
- Telecommunication facilities.
- Water pumping systems.
- Mobile facilities (caravans, boats).
- Facilities requiring high availability (e.g., defense or space applications).
How many kW does a house with photovoltaics need? The methodology for powering such a facility involves the following steps:
- Area analysis: Calculating solar radiation for the entire year, and in some cases, monthly. Unlike grid-connected systems, in off-grid systems, energy needs may vary depending on the season or time of day.
- Recording energy requirements: Each facility has different loads, so it's essential to record them and their usage duration, as well as the desired autonomy time.
- Techno-economic study: After analyzing the technical characteristics, a study of economic factors and possible subsidies follows to achieve the best technical and economic solution.


